What does ADA compliance mean for my business?
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is one of the most visible and complicated pieces of legislation in the sphere of accessibility — and it’s critical to be on top of it with respect to your digital presence. The topic isn’t easy to navigate, and the risks of not being in compliance include fines and lawsuits.
Of equal risk? If your business’s website isn’t compliant with accessibility standards, then you risk reputational damage, which is always bad news for both your brand and your bottom line.
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is one of the most visible and complicated pieces of legislation in the sphere of accessibility — and it’s critical to be on top of it with respect to your digital presence. The topic isn’t easy to navigate, and the risks of not being in compliance include fines and lawsuits.
Of equal risk? If your business’s website isn’t compliant with accessibility standards, then you risk reputational damage, which is always bad news for both your brand and your bottom line.
Ensuring digital accessibility is no longer an option — it's a necessity. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is a law in the United States that protects people with disabilities from being discriminated against. It affects how websites are made and used. Under the ADA, accessible online content is a civil right — failure to provide it exposes businesses to possible litigation.
For web developers and accessibility experts, understanding the significance of ADA compliance is critical in delivering seamless digital experiences for all users. This is important for a healthy, barrier-free business.
Following the rules can help you avoid legal trouble and keep your business safe. It also means treating people fairly by giving everyone a chance to use your website, no matter what disabilities they may have. When you follow the rules, you're showing that everyone is welcome and that you care about being responsible to society.
This article is your complete guide to learning how to follow the ADA. It gives you ideas, strategies, and practical tips to make sure your website meets legal standards and meets user expectations. It’s a useful first stop for web developers and ADA coordinators who are charged with implementing ADA compliance strategies within an organization.
ADA compliance and its impact on digital accessibility
ADA compliance is very important for digital accessibility. It makes sure that everyone, including people with disabilities, can use websites in the United States. It's the law for businesses and organizations.
The ADA says that all public websites must be accessible. This means that everyone can use them, no matter what their disability. It also means that businesses and web developers need to make sure their digital content is inclusive and doesn't have any barriers for people with disabilities.
ADA compliance is about more than just following the law. It's about making sure that everyone has equal access to information and services online. If a business doesn't follow the ADA, they could get sued and their reputation could be hurt.
For web developers, ADA compliance isn't just about checking off a list of requirements. It's about building websites that are ethical and easy to use for everyone. This includes things like making sure the website is easy to navigate, the text is easy to read, and all multimedia is accessible.
Understanding ADA compliance
ADA regulations can seem complex, but they’re essential for creating accessible digital environments. At its core, ADA requirements ensure websites are usable by individuals with disabilities.
The Department of Justice enforces the ADA through investigations, complaints, and lawsuits. Lawsuits are typically the result of significant violations where complaints fail, and there are penalties and damages for noncompliance.
Note: In addition to the ADA, there's Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act. This part of the Act focuses on making electronic and information technology easier for people with disabilities to use. It's more specific to the federal government and companies that work with it.
To make sure your websites follow Section 508, you can start by learning about the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.1 (WCAG). These are rules for making websites accessible for everyone. They cover things like how easy it is to read text, use the keyboard to navigate, and access multimedia. By following these guidelines, you can make websites that are ADA compliant and easy to use.
Siteimprove’s free accessibility checker can scan your site against Section 508 requirements. It’s also worth exploring the ADA’s own resources on website compliance .
Importance of Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
WCAG presents a structured approach to crafting inclusivity online. Established by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), these guidelines focus on four key principles: Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust (POUR).
- Perceivable: Information should be presented in ways users can perceive it. This involves providing alternative text for images, offering transcripts for audio, and making content navigable via text readers.
- Operable: User interface components and navigation must be usable. This includes features like keyboard accessibility, avoiding content that may induce seizures, and offering enough time for users to read and use the content.
- Understandable: Information and the operation of the user interface must be comprehensible. Use predictable web pages, assistive instructions, and clear language to make interactions seamless.
- Robust: The content must be comprehensible through various user agents, including assistive technologies. Content must adapt as technology evolves.
When you fully adhere to these principles, you’re poised to deliver digital content that users can recognize and interact with, regardless of their disabilities.
Within WCAG , there are three levels of conformance: A, AA, and AAA, with A as the minimum requirement.

Level A (Minimum Accessibility)
These are the most basic web accessibility features, and they’re key to preventing barriers that block access entirely. Failing to meet Level A criteria can make it impossible for some users with disabilities to access content.
Examples of requirements :
- Non-text content : Provide text alternatives for non-text elements (e.g., images must have alt text).
- Keyboard access : All functionality must be operable through a keyboard interface without requiring specific timing.
- Navigation : Ensure pages have a title describing their purpose.
- Errors : Identify errors in input forms (e.g., when a required field is left empty).
Level AA (Enhanced Accessibility)
Level AA builds on Level A by fixing the most common problems that affect user experience, especially users with low vision or mental disabilities. In many countries, Level AA is the standard for legal and regulatory compliance.
Examples of (AA) requirements :
- Contrast ratio : Text and images must have a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 for readability.
- Resizable text : Content should be scalable up to 200% without losing functionality or clarity.
Navigation consistency : Menus and navigation should be presented in a consistent order.
- Labels and instructions : Form fields should include clear labels and instructions.
- Alt text accuracy : Beyond providing alt text, it should also meaningfully describe content.
Think of it this way: Level A ensures basic accessibility by making content accessible at a basic level. Level AA focuses on usability and inclusivity to improve access and user experience for more people.
Then there's Level AAA, the highest level, which includes the most strict accessibility needs, sign language interpretation, adjustable line spacing, and longer audio descriptions. It's not usually required for full compliance in most cases (but will probably be soon).
Designing for accessibility
Designing for web accessibility means following best practices to help all users, no matter their abilities. Inclusive design is a basic principle that focuses on creating easy-to-use digital experiences for different types of users. This approach ensures websites are usable by people with disabilities and provides equal access to information and services.
Universal design goes a step further by making products and environments easy for everyone to use without needing changes. Web developers can use accessible design tools to improve user experiences, ensuring websites are intuitive and easy to navigate. By following these principles, developers can create inclusive and accessible digital spaces.
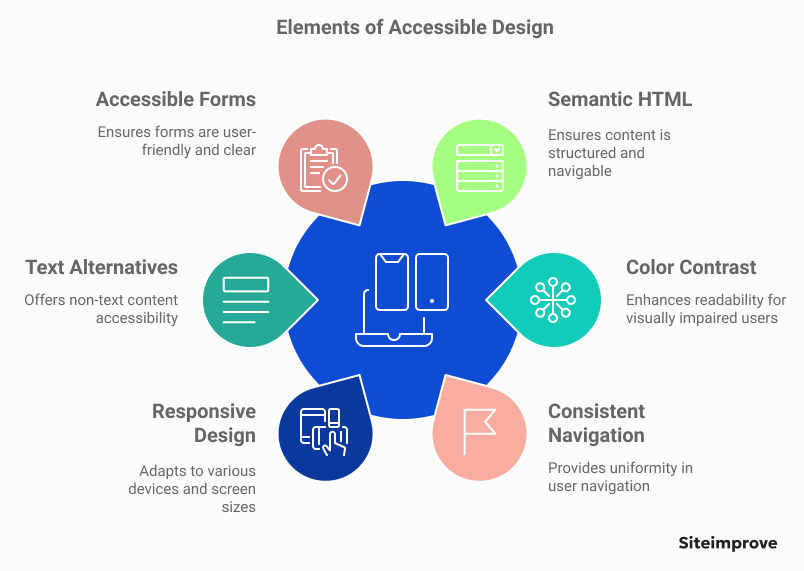
Key elements of accessible design
An accessible design comprises several critical elements that must be integrated into the web development process:
- Semantic HTML: Using HTML markup correctly ensures that assistive technologies accurately interpret content. Tags like `<header>`, `<nav>`, `<article>`, and `<footer>` improve the structure and navigability of web pages.
- Color Contrast: Websites must have enough contrast between text and background colors to ensure readability for users with visual impairments. Tools like contrast checkers can verify the adequacy of color choices.
- Consistent Navigation: Uniformity in navigation helps users understand and predict navigation patterns across the website, improving user experience.
- Responsive Design: Ensuring compatibility across devices is vital. Designs should be flexible, responding intuitively to different screen sizes and orientations without compromising accessibility.
- Text Alternatives: All non-text content should have a text alternative, like captions for videos or alt text for images. This will make sure that information isn't lost for users who need text.
- Forms and Fields: Forms should be accessible, with clear labels and instructions. Error messages should be descriptive, guiding users in correcting inputs.
Leveraging technology for accessibility
Assistive technology is important for making digital content accessible to people with disabilities. These tools, such as screen readers or voice recognition, help people use websites in ways that are easier for them. To make websites and apps accessible, these tools need to be added to them so that everyone can use them.
Mobile accessibility tools, such as iOS VoiceOver and Android TalkBack, are also very important. People with disabilities use different devices, including phones and tablets, to access websites. So developers can use these tools to make sure their websites work well on these devices. By making websites accessible on both computers and mobile devices, developers can create digital experiences that include everyone.
Types of assistive technology
Implementing effective assistive technologies is critical to fulfilling ADA compliance. Some prevalent technologies include:
- Screen readers: Convert text displayed on a screen into speech or Braille output. Examples include Job Access With Speech (JAWS) and NonVisual Desktop Access (NVDA).
- Braille displays: These output devices translate text into Braille, enabling users with visual impairments to read digital content through touch.
- Voice recognition software: L ets users control devices and type text by speaking. This is a different way for people with mobility problems to interact.
- Screen magnifiers: Magnify portions of the screen to enhance visibility for users with low vision, providing better clarity for viewing web content.
Audits for compliance
Conducting an accessibility audit is a critical step in ensuring ADA compliance. This process is about looking at a website's accessibility features and finding ways to improve them. It's best when accessibility audit tools are used because they give you information about compliance problems and help you fix them. They’re a cost-effective way to make sure that websites meet legal standards and provide accessible experiences for all users.
Conducting an accessibility audit
The audit process checks for things that might stop users from accessing web content. First, existing content is checked against accessibility standards.
Then, tools like Siteimprove’s ADA compliance checker can find issues like missing descriptions or incorrect labels.
But we can't just use these tools. Testing by people with disabilities or that copies how people with disabilities use websites can find other problems, such as difficulty in navigation.
Using both automated and manual audits helps us understand how accessible a website is.
Siteimprove offers both automated and manual testing .
Benefits and Challenges of ADA Compliance
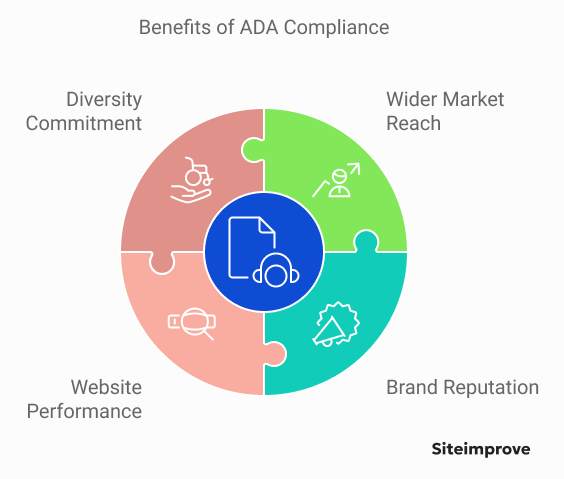
Embracing ADA compliance gives businesses many benefits beyond just following the law.
- Reach a wider market — By making websites and digital content accessible, companies can reach more customers, including people with disabilities who make up a large part of the consumer base.
- Boost brand reputation and customer loyalty — Accessible websites are seen as more user-friendly and trustworthy, which can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improve website performance and SEO — Accessible websites are often easier to use for all users, which can improve website performance and search engine rankings.
- Show commitment to diversity and inclusion — Focusing on accessibility shows that a company cares about diversity and inclusion, which is important to many consumers.
Businesses may face challenges when trying to become ADA compliant, such as:
- Lack of awareness or understanding of accessibility standards among development teams
- Perceived cost of compliance
Solutions to these challenges
- Provide comprehensive training and education programs to development teams
- Integrate accessibility into the development process from the start to reduce long-term costs
- Use automated tools to find accessibility problems early and do regular audits
How to address common challenges in ADA compliance
To follow ADA rules, businesses should take a proactive approach. To understand how users with disabilities use your product, involve them in the design and testing stages. This will ensure that your solutions meet their needs.
Working with accessibility experts can give you guidance and support. Making accessibility a part of your company's culture can make it easier to follow the rules and create an environment that includes everyone and encourages innovation in all areas of your business.
Conclusion
Making sure our digital spaces follow the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) isn't just about the law. It's about making sure everyone can use and enjoy them.
When businesses make their websites and apps easy to use for people with disabilities, they're not only doing the right thing, they're also smart. They're reaching a wider audience and building a better reputation.
Making our digital world more accessible isn't always easy. But it's worth it. When we make things easier for everyone, we all benefit.
There are a few things businesses can do to make their digital spaces more accessible. They can:
- Train their employees on how to make their content accessible.
- Use design principles that make it easy for people with disabilities to use their websites and apps.
- Work with people with disabilities to make sure their products and services meet their needs.
By making our business practices more accessible, we can create a more inclusive and welcoming digital world for everyone.
FAQs
What are the basic requirements of ADA?
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) says that people with disabilities should have the same chances as everyone else. This means making sure that people with disabilities can get jobs, go to public places, and use phones and computers. The goal is to stop discrimination and make sure that people with disabilities can easily get around and do things.
What's an ADA compliance example?
An example of ADA compliance is when a business puts in ramps and elevators so people who use wheelchairs can get around. In the digital world, it could mean making a website that people with screen readers can use easily. This could mean adding descriptions for images, using keyboard navigation, and having clear headings so people can find what they need quickly.
What's considered a violation of ADA?
ADA violations happen when someone is not given the same chances or changes as others because they have a disability. This can mean not hiring someone because of their disability, not making buildings easy to get into, or not making websites easy to use for people who use special tools to help them.
What are the benefits of digital accessibility?
Digital accessibility is important because it:
- Reaches more people
- Makes everyone feel included
- Improves the experience for everyone
- Makes your brand look good
- Reduces the risk of legal problems
- Can help with search engine rankings
What are best practices for accessible UX design?
Best practices for accessible UX design:
- Clear, simple, and consistent navigation
- Text easy to read with enough contrast
- Text alternatives for non-text content
- Easy to navigate and understand for all, including those using assistive technologies
What's ADA compliance?
ADA compliance means following rules to make services, programs, and facilities accessible to people with disabilities. This includes making adjustments to remove barriers and ensure equal access in both physical and digital spaces.
How can businesses promote disability inclusion?
Businesses can make it easier for people with disabilities to be included by:
- Creating a welcoming and inclusive work environment
- Educating employees about disabilities
- Making sure that communication materials and the workplace are accessible to everyone
- Involving people with disabilities in decision-making
- Providing support and adjustments to meet the needs of employees and customers with disabilities
