Where form meets function,
meets performance
Our platform is purpose-built to make every website function better, from every POV. Whether you’re looking to find and fix broken links, ensure accessibility, maximize SEO, drive traffic, or simply measure it all in one place, look no further.
What makes us great
Every successful website has to work before it can engage, and engage before it can convert. That’s why we address all three — functionality, content experience, and performance — all from one platform. Here’s a snapshot of what defines the Siteimprove experience at its most foundational level.
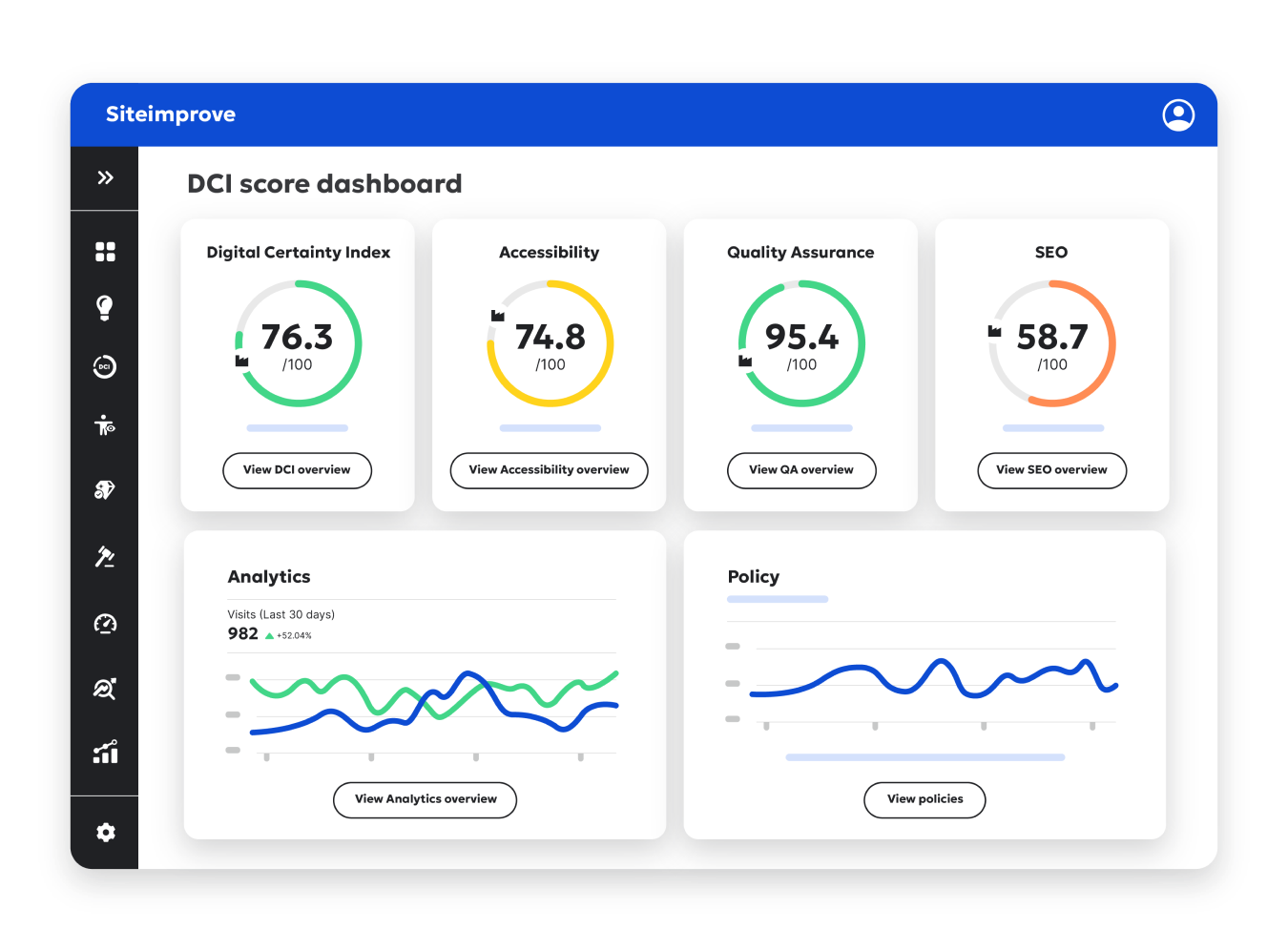
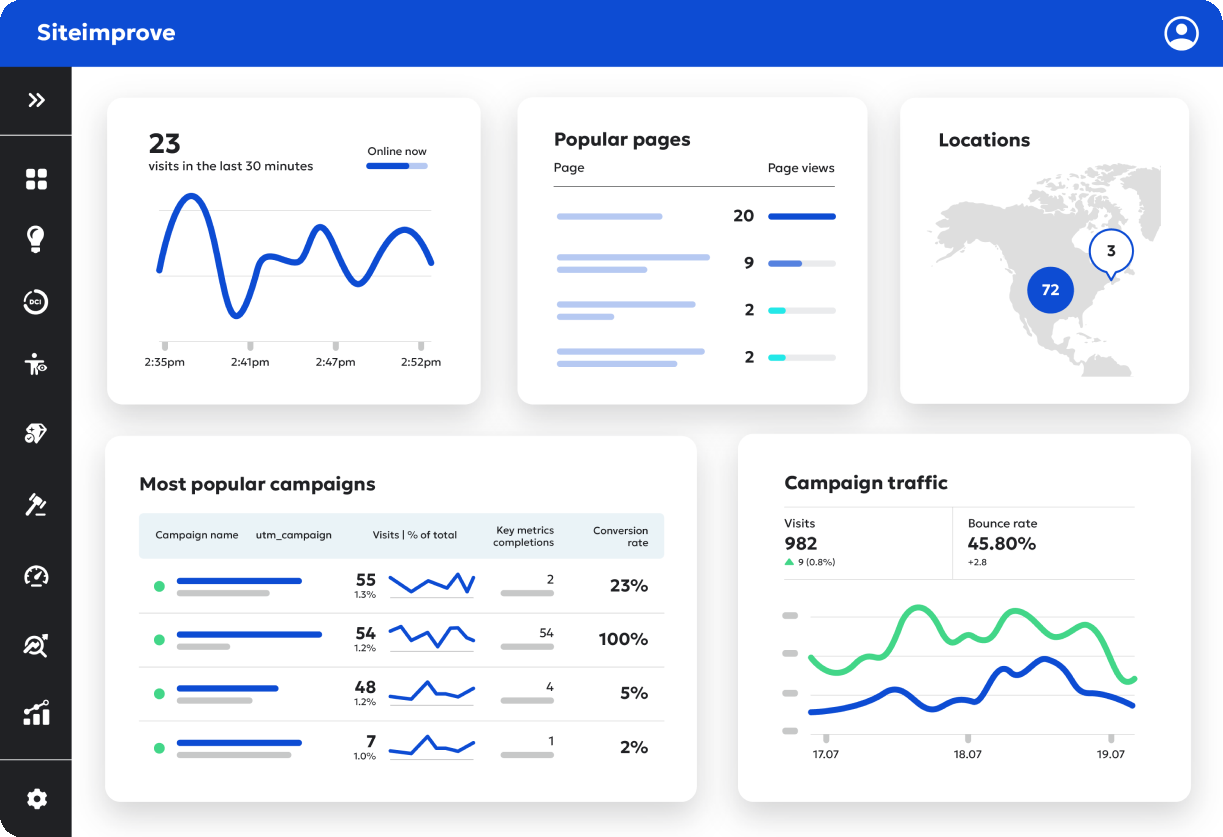
Data, meet direction
There are plenty of analytics dashboards out there, but none that serve up actionable feedback around how to improve the metrics you see like ours does. With us, you get the data, but also a sense of how your efforts compare historically as well as how they stack up against one another IRL.
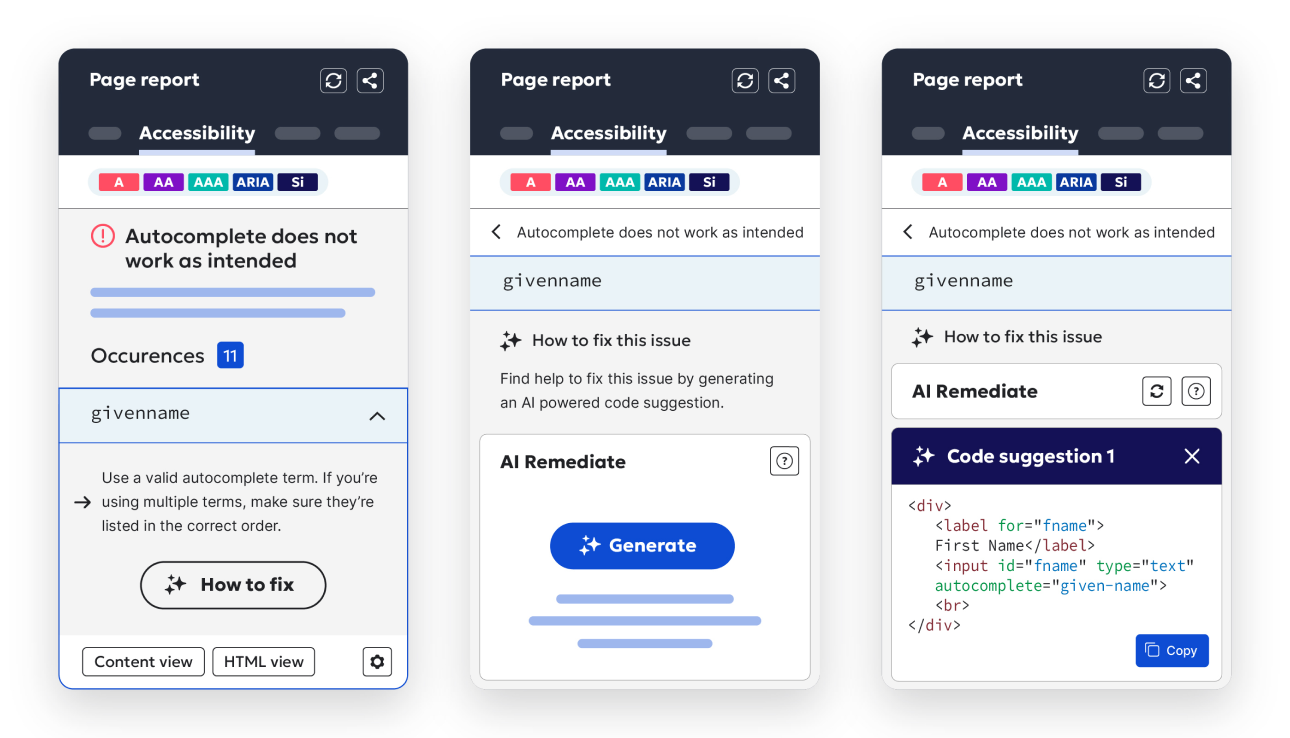
From AI generation to Generation AI
We’re leading the way in an area that is leading us all. Get AI-generated recommendations — from copy edits to code snippets — that you can choose to add right there in the CMS, or not.
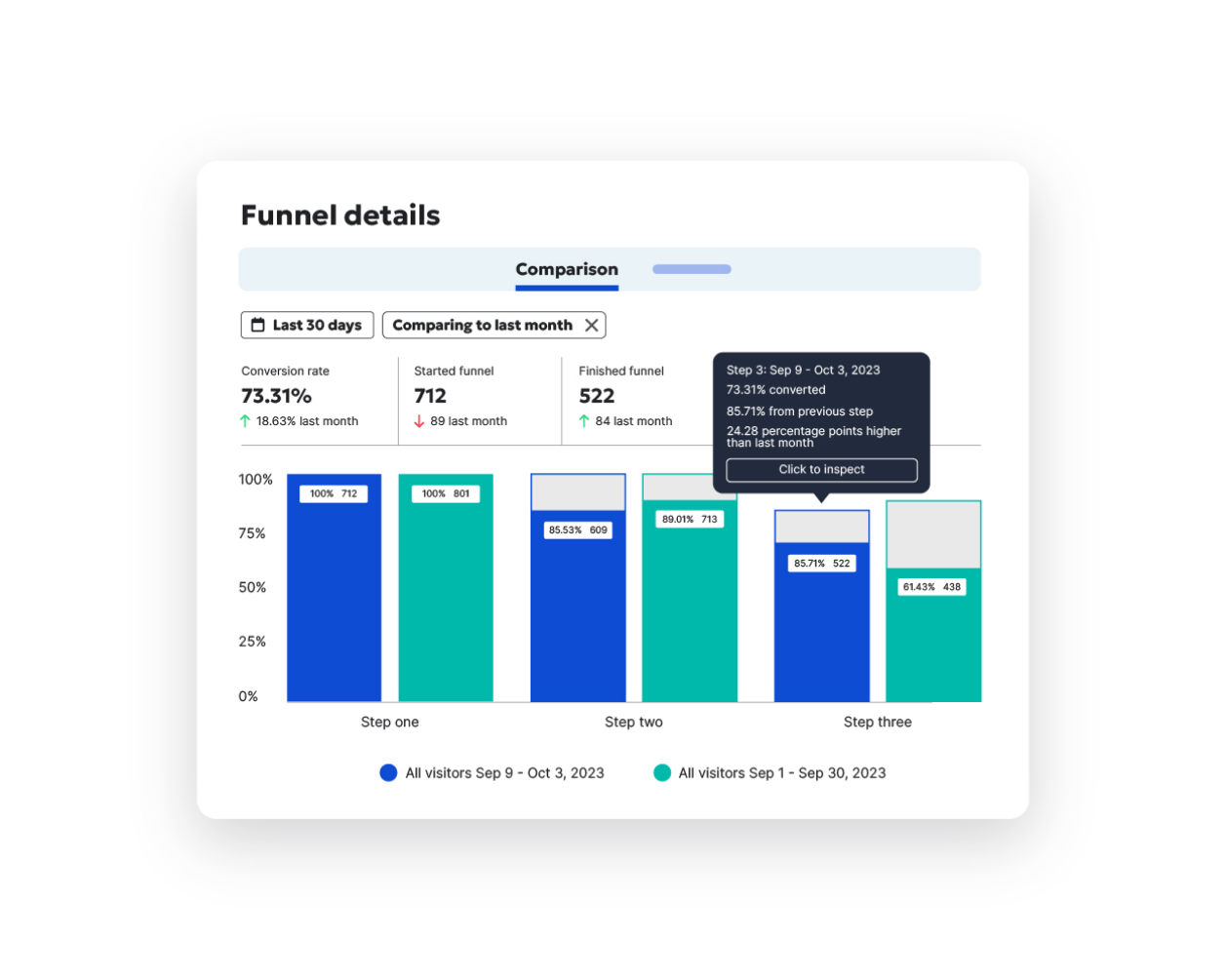
Paid and organic ROI, together at last
Plenty of point solutions focus on digital ad management, and plenty focus on SEO, but few boast an equal command of both. By making your on-site content more engaging, your ads deliver better results; by optimizing your paid efforts, you get more eyes onto your site with less spend.
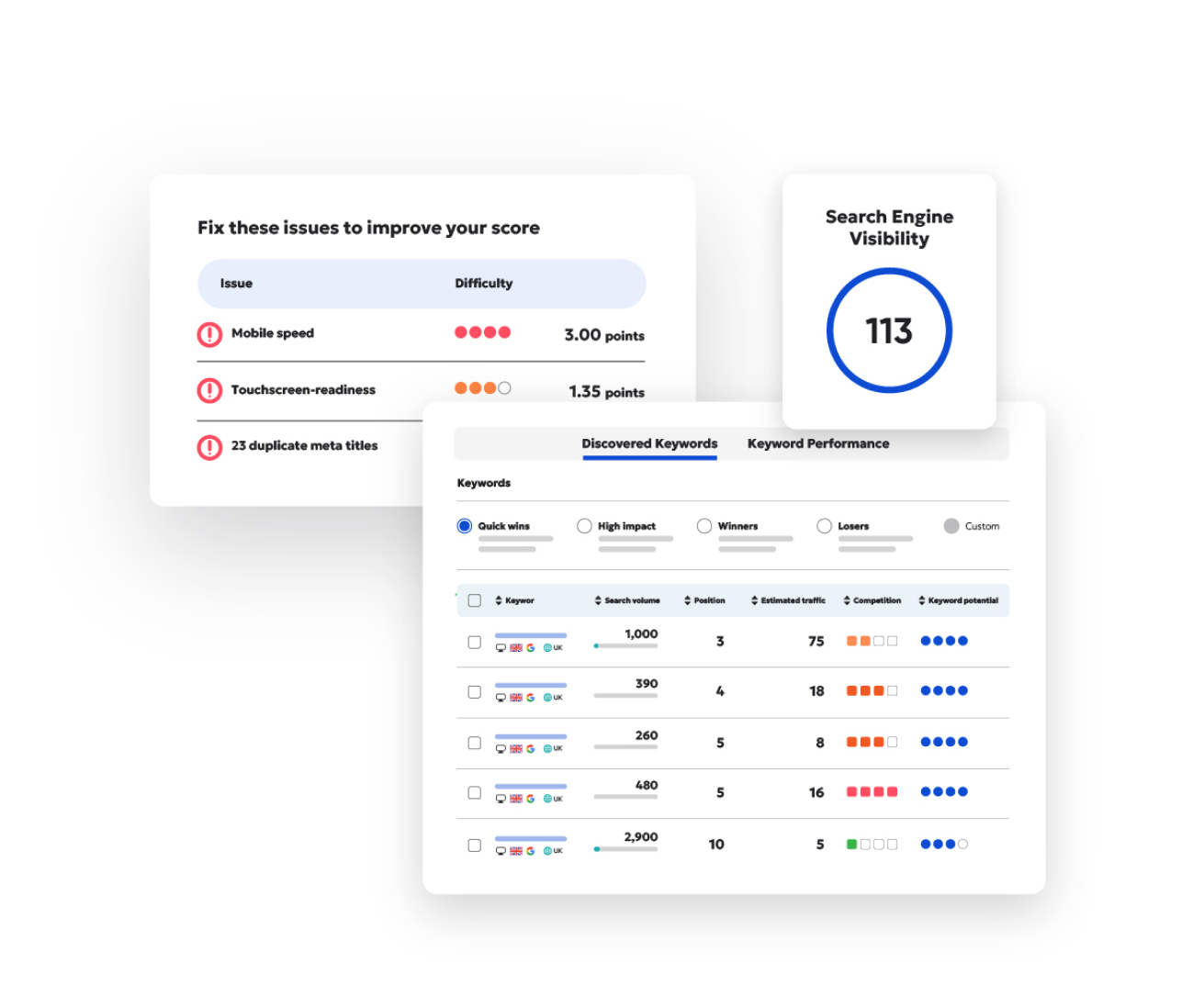
Faultless digital experiences for all
Before your website can draw a crowd, it needs to get the fundamentals right. Our automated checks identify broken links, inconsistencies, misspellings, and accessibility breaches so that every visitor to your site is guaranteed a flawless, fully inclusive experience.




All this, and we play nice with the MVPs in your stack
From browser extensions to connectors, the Siteimprove platform is designed to capitalize on industry-leading innovation, not compete with it. Have a look at the range of apps, tools, and customization opportunities we support, and how it fits into your ecosystem.