Enhancing SEO through web accessibility
Many accessibility best practices, such as using semantic HTML and optimized images, align with SEO principles, improving both user experience and search engine visibility.
- By Stephen Jeske - Mar 06, 2025 SEO
It's no secret that search engine optimization (SEO) is important. But did you know that improving accessibility for users with disabilities can significantly boost your SEO performance? This guide explains why.
Understanding Web Accessibility and Its Importance
What is Web Accessibility?
Web accessibility means designing and developing websites that everyone can use, regardless of their abilities. This includes people with visual, auditory, motor, cognitive, or neurological disabilities. It's about removing barriers that prevent anyone from interacting with online content.
Why is Web Accessibility Important for All Users?
Accessibility directly benefits people with disabilities. But it also improves the experience for everyone. Think of it this way.
Clear navigation, well-organized content, and designs that work on mobile devices help everyone. A site that's easy to use with a screen reader is also easier for someone with a slow internet connection or on a mobile phone.
By making your website accessible, you attract more people, including those with disabilities. That gives you broader reach.
Accessible design often means a more intuitive and easy-to-use experience. This leads to more engagement and satisfaction.
How Does Web Accessibility Align with SEO Principles?
The great news is that many accessibility best practices directly overlap with SEO best practices. Both aim to create a positive user experience and make it easy for search engines to understand and index your content. Here's how they connect:
- Structured Content: Using semantic HTML, clear headings, and clear link text helps both people who use assistive technology and search engines. This makes your content easier to understand and find.
- Optimized Images: Alt text for images is important for accessibility. Screen readers use it. It also helps search engines understand images, which improves image SEO.
- Improved Crawlability: Accessible websites are often easier for search engine bots to crawl and index. This can lead to better visibility in search results.
- Focus on User Experience: Both accessibility and SEO prioritize user experience. By making your website easy to use, you improve how people feel when they visit. This is important for search engines. When people like a site, they stay longer, visit more pages, and do more things there. Search engines notice this and may rank your site higher.
WCAG: The Foundation of Accessible SEO
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). They are the global standard for making web content accessible. Adhering to WCAG not only makes your site accessible but also provides a solid foundation for SEO success. Many WCAG guidelines, like clear headings and descriptive link text, directly benefit SEO.
There are five ways in which improvements to website accessibility can positively affect SEO.
- Improved Crawlability: Search engine bots "crawl" websites to understand their content. Just like assistive technologies, these bots rely on well-structured content. Use semantic HTML, add alt text to images, and use Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA) attributes. Making your site easier for both bots and assistive technologies to understand can lead to better search rankings.
- Enhanced User Engagement: Accessible websites are more user-friendly for everyone. Clear navigation, easy-to-read text, and logical structure contribute to a positive user experience. This means people stay on the site longer, click fewer times to leave, and look at more pages. These are important things search engines look at when ranking websites.
- Better Content Discoverability: Use descriptive page titles, structured data, and transcripts for multimedia. Help search engines understand and index your content more effectively. It makes it easier for your target audience to find your website in search results.
- Mobile Friendliness: Many features that help with accessibility, such as responsive design and good touch target sizes, are also important for mobile devices. With Google using mobile-first indexing, making your site accessible often helps with mobile SEO too.
- Alignment with Core Web Vitals: Improving accessibility often helps Core Web Vitals too. Fixing images, writing clean code, and avoiding layout shifts can make your site more accessible and improve user experience. This can lead to higher rankings.
How Improving Accessibility Helps Core Web Vitals
While Core Web Vitals don't directly measure accessibility, there's a strong correlation between accessibility improvements and better Core Web Vitals scores. Here's why:
- Performance and Accessibility Overlap: Many accessibility best practices naturally lead to improved website performance, which is a key factor in Core Web Vitals. For example:
- Optimized Images: Using the right size and compressed images makes it easier for users with low bandwidth or screen readers to read. It also speeds up page load time, which helps LCP.
- Clean Code: Well-structured, semantic HTML and efficient CSS not only make sites more accessible to assistive technologies but also improve rendering performance, which can positively impact LCP and CLS.
- Reduced Motion: Providing controls for animations and transitions is important for users with vestibular disorders. Limiting excessive animations also reduces the complexity of page rendering, which can improve CLS.
- User Experience Focus: Both accessibility and Core Web Vitals prioritize a positive user experience. When you make a website accessible, you're considering the needs of all users, including those with disabilities. This often leads to a smoother, more efficient experience for everyone, which is reflected in better Core Web Vitals.
- Visual Stability and Accessibility: CLS, which measures unexpected layout shifts, is directly related to accessibility. Users with visual or cognitive impairments rely on consistent page layouts. Minimizing CLS makes the website more usable for everyone, but especially for those with disabilities.
- Responsiveness and Inclusivity: FID measures how quickly a page responds to user interaction. An accessible website is designed to be responsive and inclusive. This allows visitors with various abilities to interact with the page efficiently. This responsiveness naturally leads to better FID scores.
By focusing on accessibility, you're creating a website that's well-structured, efficient, and user-friendly for everyone. These qualities are also the foundation for good Core Web Vitals. So, while not a direct cause-and-effect relationship, prioritizing accessibility often results in a website that performs better and scores higher in Core Web Vitals.
Drive SEO Performance with Siteimprove's Accessibility Insights
Maintaining website accessibility can feel daunting, but it doesn't have to be. Siteimprove offers a powerful platform that simplifies the process, helping you identify and address accessibility issues while simultaneously boosting SEO performance. The accessibility checks directly contribute to SEO improvements in several key ways.
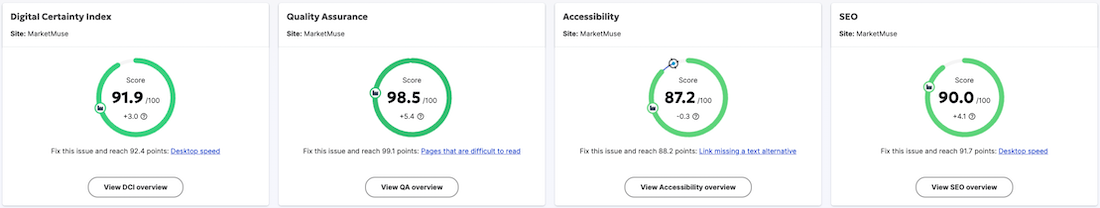
Identifying Technical SEO Issues: Siteimprove's crawlers find technical problems that make it hard to read, like broken links, missing alt text, and wrong use of headings. These issues often overlap with technical SEO problems, and fixing them improves both accessibility and search engine crawlability.
Optimizing Image Alt Text: Siteimprove helps you ensure that all images have descriptive alt text. As we've discussed, alt text is vital for both accessibility (screen readers) and SEO (image indexing). Siteimprove not only identifies missing alt text but also helps you write effective, keyword-relevant descriptions.
Improving Content Structure: Siteimprove looks at your content structure and points out problems like missing or wrong headings. Using headings correctly is important for people using screen readers and for search engines to understand your content better.
Improving User Experience: By helping you make your website easier to use, Siteimprove improves user experience. This means fewer people leave quickly — they stay longer, and they interact more. These are all good things for search engines.
Streamlining the Accessibility Workflow: Siteimprove provides clear reports and prioritized recommendations, making it easier to address accessibility issues efficiently. This saves you time and resources while ensuring your website meets accessibility standards and SEO best practices.
Leverage Siteimprove for SEO Accessibility
Here’s how Siteimprove can help with both accessibility and SEO.
- Regular Scans: Schedule regular scans of your website to identify new and recurring accessibility issues.
- Prioritize Issues: Siteimprove prioritizes issues based on severity and impact. Focus on the most critical issues first to maximize your impact on both accessibility and SEO.
- Actionable Insights: Siteimprove provides clear explanations of each issue and offers step-by-step instructions on how to fix them.
- Integrate with Your Workflow: Integrate Siteimprove into your content creation and development workflows to ensure accessibility is considered from the beginning.
- Monitor Progress: Track your progress over time to see how your accessibility improvements impact SEO performance.
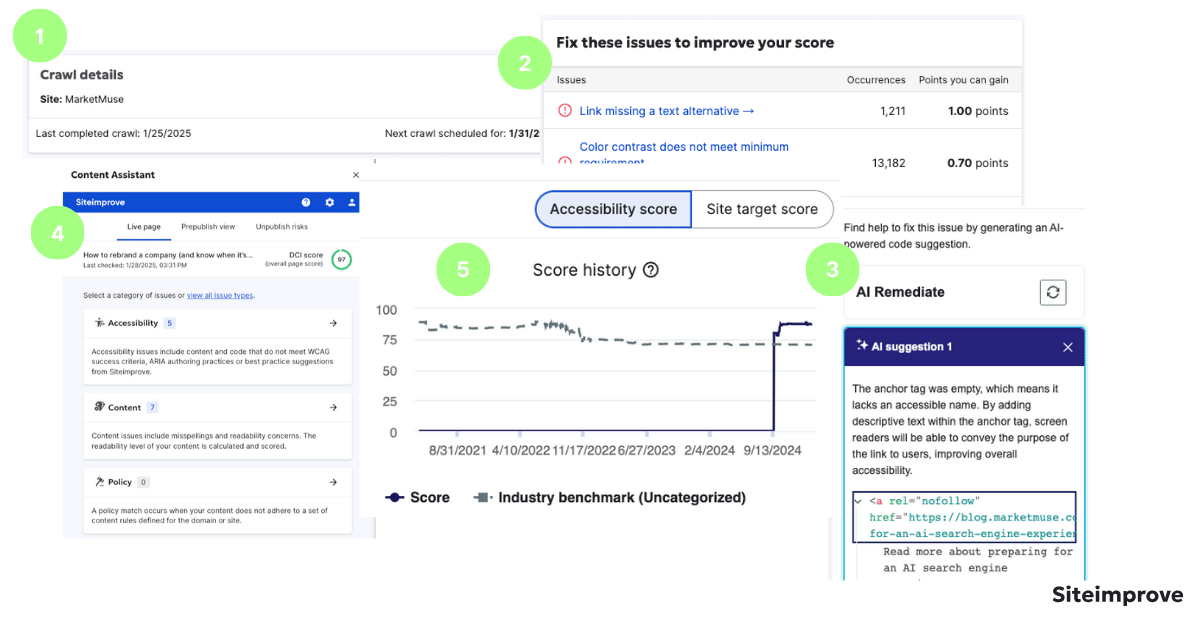
While I've talked about how accessibility helps SEO, it's important to know that Siteimprove also has specific SEO tools. They can help with keyword research, on-page optimization, and technical SEO audits. All work together to make your SEO strategy even stronger.
Best Practices for Implementing SEO Accessibility
Use this convenient website accessibility checklist to start:
- Use Semantic HTML: Ensure your website uses proper HTML tags that convey the structure and meaning of the content. This helps search engines understand the context and improves the experience for users with assistive technologies.
- Alt Text for Images: Provide descriptive alt text for all images. This helps visually impaired users understand the content. Plus, it gives search engines more information about the images, boosting your SEO.
- Keyboard Navigation: Make sure your website is fully navigable using a keyboard. This is essential for users who can't use a mouse and helps search engines understand the structure and flow of your site.
- Clear and Consistent Navigation: Use clear and consistent navigation labels and structures. This makes it easier for users and helps search engines understand which pages are more important.
- Headings and Subheadings: Use headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to structure your content. This helps both users and search engines understand the organization of the page.
- ARIA Roles and Landmarks: Use them to enhance the accessibility of dynamic content and complex user interfaces.
- Color Contrast: Ensure that text and background colors have sufficient contrast. This improves readability for all users and can prevent issues that might affect user engagement and bounce rates.
- Accessible Forms: Make sure forms are easy to use and understand. Label all form fields clearly and provide error messages that are easy to understand.
- Video and Audio Transcripts: Provide transcripts for video and audio content. This helps users who are deaf or hard of hearing and provides additional text content for search engines to index.
- Regular Audits: Regularly audit your website for accessibility issues using Siteimprove. Address any issues quickly to maintain a high level of accessibility and SEO performance.
Conclusion: Building a More Accessible and SEO-Friendly Web
I hope I've shown the powerful synergy between web accessibility and SEO. By focusing on accessibility, you make your online content more inclusive and improve your SEO. The benefits are clear: better search engine crawling, more user engagement, easier content discovery, mobile-friendliness, and better Core Web Vitals. It’s not just the right thing to do — it’s also smart for your website’s visibility and reach.
Implementing What You've Learned
The knowledge shared in this guide can be put into action immediately. Here's a practical approach:
- Assess Your Current State: Begin with an accessibility audit using Siteimprove, as discussed in the guide. This will provide a clear picture of your website's current accessibility level and highlight areas for improvement.
- Prioritize and Plan: Don't try to fix everything at once. Siteimprove's prioritization features will help you focus on the most impactful issues first. Create a plan to address these issues systematically.
- Integrate Accessibility into Your Workflow: Make accessibility a part of your website development and content creation processes. Siteimprove makes it easy. Train your team on accessibility best practices. Ensure that everyone understands their role in creating an inclusive online experience.
- Leverage Siteimprove: Use Siteimprove's comprehensive features for ongoing monitoring, testing, and reporting. Actionable insights and a streamlined workflow make it easier to maintain accessibility and track your progress.
- Focus on the Fundamentals: Remember the core principles of accessible SEO. That's semantic HTML, descriptive alt text, keyboard navigation, clear navigation, and well-structured content. These are the building blocks of both accessibility and SEO success.
Next Steps for Continued Improvement
Accessibility is an ongoing journey, not a destination. Here are some key next steps to ensure your website remains accessible and continues to reap the SEO benefits.
Regularly Audit and Test: Conduct regular accessibility audits using Siteimprove. That will help catch any new issues and ensure your website stays compliant. Don't forget to test with real users, including people with disabilities, to get valuable feedback.
Stay Informed: Accessibility guidelines and best practices are constantly evolving. Stay up-to-date with the latest WCAG updates and SEO trends to ensure your website remains compliant and competitive.
Educate Your Team: Invest in ongoing training for your team on accessibility best practices. The better they understand accessibility, the more they can make content that includes everyone and is SEO-friendly.
Embrace an Inclusive Mindset: Accessibility isn't just a technical checklist. It's about creating a web that's usable and enjoyable for everyone. Embrace an inclusive mindset in all aspects of your website development and content creation.
By focusing on accessibility, you improve your website’s SEO and help create a more inclusive digital world. Start today, and you'll see the positive impact on both your users and your search engine rankings.
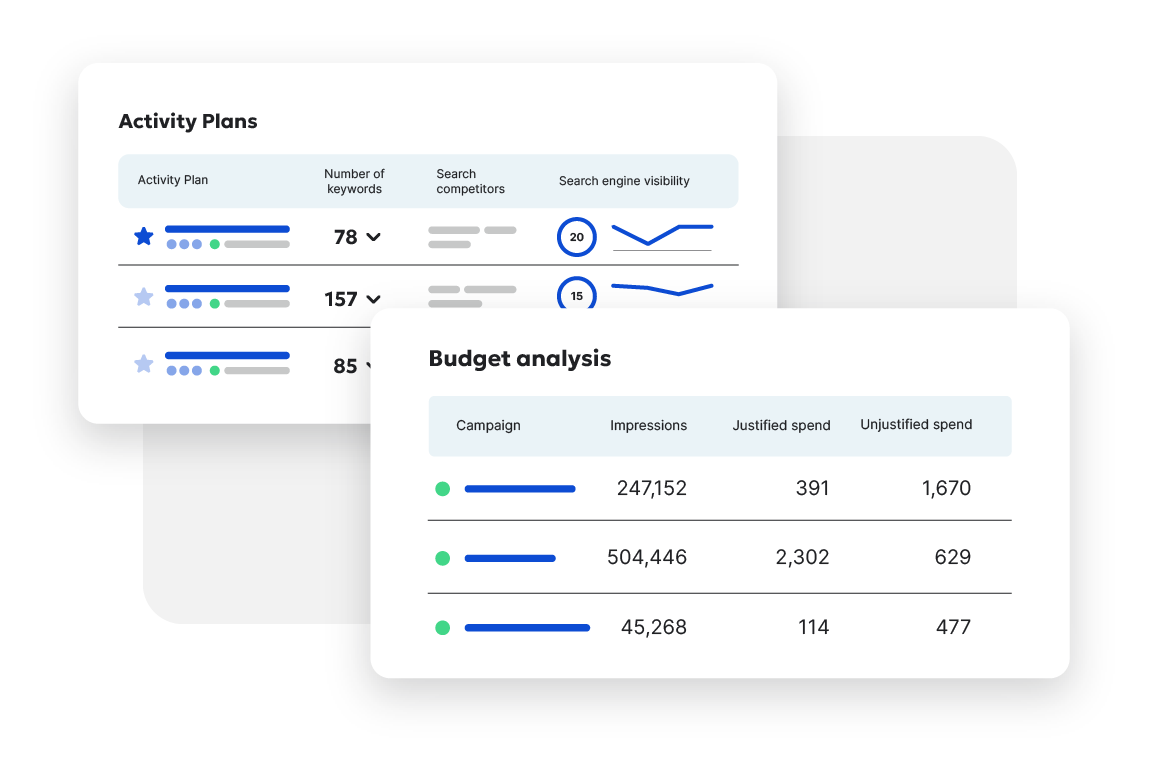
Ready to improve your Search Engine Optimization?
Siteimprove SEO is an all-in-one Enterprise SEO tool that can help you achieve your digital potential.
Schedule a demo
